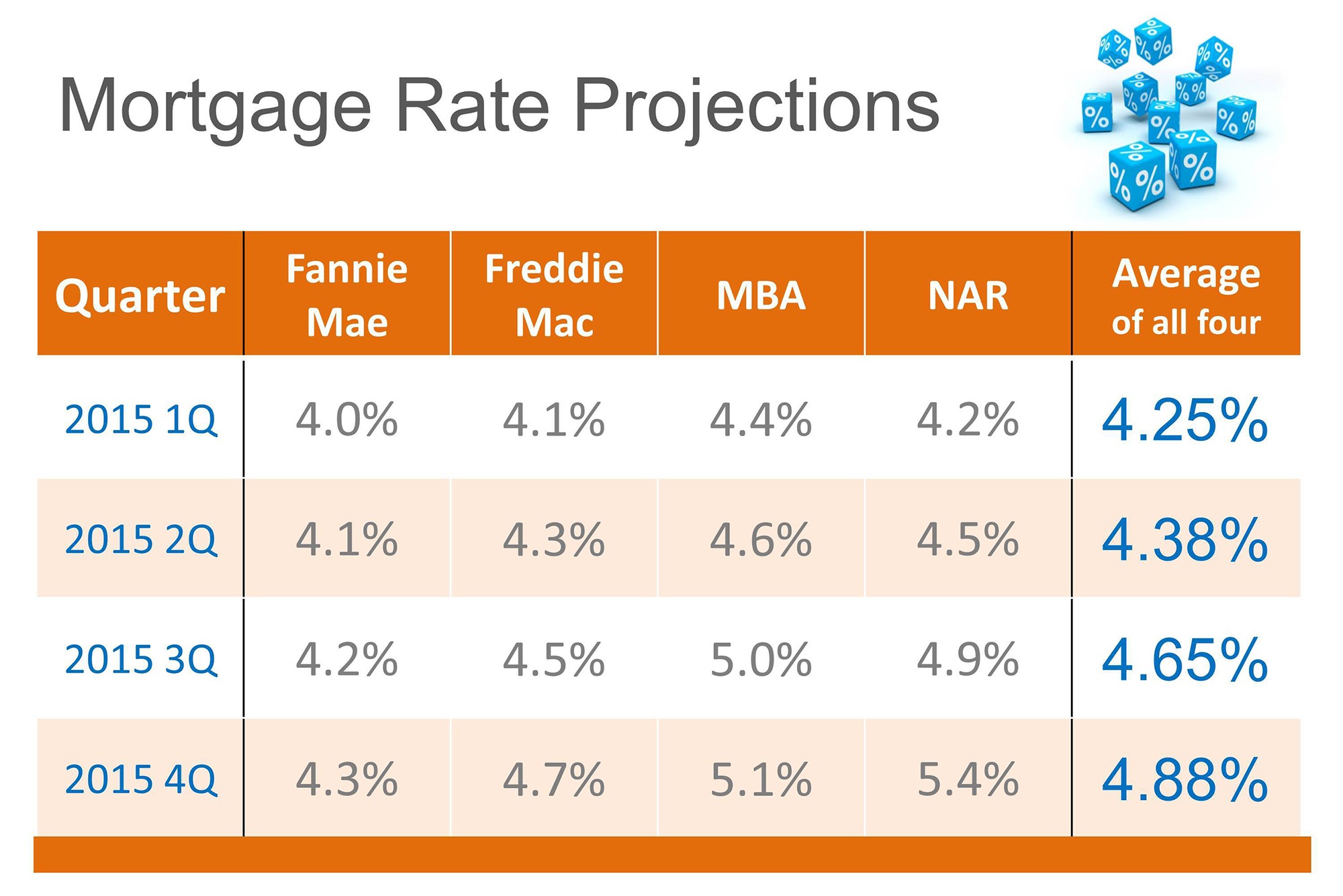
Home loan interest rates take center stage in the realm of personal finance, shaping the decisions of countless individuals looking to purchase or refinance their homes. Understanding the nuances of these rates is crucial for making informed financial choices.
Delving into the intricacies of how these rates are determined, the types available, and the factors influencing them can provide valuable insights into securing the best possible deal on a home loan.
Overview of Home Loan Interest Rates
Home loan interest rates refer to the percentage charged by lenders for borrowing money to purchase a home. It is a crucial factor that determines the overall cost of the loan and affects monthly payments.
How Home Loan Interest Rates are Determined
Home loan interest rates are determined by various factors, including:
- The Reserve Bank of India’s monetary policy
- Market conditions and economic indicators
- Lender’s operational costs and profit margins
- Borrower’s credit score and financial history
Factors Influencing Home Loan Interest Rates
Several factors can influence home loan interest rates, such as:
- Current economic conditions
- Inflation rates
- Global economic trends
- Type of loan (fixed-rate or adjustable-rate)
Types of Home Loan Interest Rates
When it comes to home loan interest rates, borrowers often have the choice between fixed and variable rates. Each type has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, and understanding the differences can help borrowers make an informed decision based on their financial goals and circumstances.
Fixed Interest Rates
Fixed interest rates remain the same throughout the entire term of the loan, providing borrowers with predictability and stability in their monthly payments. This type of rate is ideal for individuals who prefer budget certainty and want to protect themselves from potential interest rate hikes in the future. For example, a borrower who plans to stay in their home for a long period of time may benefit from a fixed interest rate as it offers peace of mind knowing that their payments will not change.
Variable Interest Rates
Variable interest rates, on the other hand, fluctuate based on market conditions, which means that monthly payments can vary over time. While this type of rate may initially offer lower interest rates compared to fixed rates, there is also the risk of payments increasing if interest rates rise. Variable rates are suitable for borrowers who are comfortable with some level of uncertainty and are willing to take on the risk of potential rate increases. For example, a borrower who plans to sell their home in a few years may opt for a variable rate to take advantage of lower initial payments.
Overall, the choice between fixed and variable interest rates ultimately depends on the borrower’s individual financial situation, risk tolerance, and long-term plans for their property. It’s important for borrowers to carefully consider their options and consult with a financial advisor before deciding on the type of interest rate that best suits their needs.
Factors Affecting Home Loan Interest Rates
When it comes to home loan interest rates, several factors come into play that can influence the rates offered to borrowers. Understanding these factors is crucial for anyone looking to secure a home loan at the best possible rate.
Economic Factors Impacting Home Loan Interest Rates
- Economic Growth: Strong economic growth typically leads to higher home loan interest rates as demand for loans increases.
- Employment Rates: Low unemployment rates can result in higher interest rates, as lenders may see less risk in lending money.
- Market Forces: Supply and demand dynamics in the housing market can also impact interest rates as lenders adjust rates based on market conditions.
Influence of Inflation Rates on Home Loan Interest Rates
-
Inflation rates play a significant role in determining home loan interest rates. When inflation is high, lenders may increase interest rates to offset the decrease in purchasing power of the loan amount over time.
- Conversely, low inflation rates may result in lower interest rates to stimulate borrowing and spending.
Role of Central Banks in Setting Home Loan Interest Rates
- Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, play a crucial role in setting short-term interest rates, which can indirectly influence home loan interest rates.
- By adjusting monetary policy, central banks can impact the overall economy, including interest rates, to achieve specific economic goals.
- Changes in central bank interest rates can lead to corresponding changes in home loan interest rates offered by financial institutions.
Comparison of Home Loan Interest Rates Across Lenders
When looking to secure a home loan, it is essential to compare interest rates from different lenders to ensure you are getting the best deal possible. Here is a guide on how to effectively compare home loan interest rates and make an informed decision.
Considering Fees and Charges
- Look beyond the interest rate: While the interest rate is a crucial factor, don’t forget to consider additional fees and charges associated with the loan. These could include application fees, annual fees, valuation fees, and legal fees.
- Calculate the comparison rate: The comparison rate combines the interest rate and most fees and charges to give you a better overall picture of the cost of the loan. This can help you compare different loan products more accurately.
- Consider ongoing costs: Some loans may have lower interest rates but higher ongoing fees, which can add up over time. Make sure to factor in these ongoing costs when comparing loan options.
Negotiating for Better Rates
- Research and compare: Before negotiating with a lender, do your research and have a clear understanding of the current market rates. This will give you leverage during negotiations.
- Highlight your financial stability: Lenders are more likely to offer better rates to borrowers with a stable income, good credit history, and a low debt-to-income ratio. Highlighting these factors can help you negotiate for a lower rate.
- Consider professional assistance: If negotiation is not your strong suit, you can consider hiring a mortgage broker to help you secure the best possible deal. Brokers have the expertise and industry knowledge to negotiate on your behalf.
Trends in Home Loan Interest Rates
Home loan interest rates have shown a fluctuating trend over the years, influenced by various factors such as economic conditions, inflation rates, and central bank policies.
Historical Trends in Home Loan Interest Rates
Historically, home loan interest rates have experienced both highs and lows. For example, in the 1980s, interest rates were as high as 18-20%, while in recent years, rates have been at historic lows of around 3-4%.
Impact of Global Events on Home Loan Interest Rates
Global events such as economic crises, geopolitical tensions, and pandemics can have a significant impact on home loan interest rates. For instance, the 2008 financial crisis led to a decrease in interest rates to stimulate the economy.
Future Trends in Home Loan Interest Rates
Based on current economic indicators, it is predicted that home loan interest rates may gradually rise in the near future. Factors such as inflation, employment rates, and government policies will play a crucial role in determining the direction of interest rates.
Impact of Credit Score on Home Loan Interest Rates
Having a good credit score is crucial when it comes to securing a favorable home loan interest rate. Lenders use your credit score to assess your creditworthiness and determine the risk of lending you money.
Relationship between Credit Scores and Home Loan Interest Rates
Your credit score directly affects the interest rate you will be offered on a home loan. A higher credit score typically results in a lower interest rate, while a lower credit score may lead to a higher interest rate. Lenders see borrowers with higher credit scores as less risky, so they reward them with better rates.
Tips to Improve Credit Scores for Lower Interest Rates
- Make sure to pay your bills on time to avoid late payments, which can negatively impact your credit score.
- Keep your credit card balances low and try to pay off any outstanding debt to lower your credit utilization ratio.
- Regularly check your credit report for errors and dispute any inaccuracies to maintain an accurate credit profile.
- Avoid opening multiple new credit accounts in a short period, as this can lower your average account age and potentially harm your credit score.
Credit History’s Influence on Home Loan Applications
In addition to credit scores, lenders also consider your credit history when evaluating your home loan application. A strong credit history, with a track record of responsible borrowing and timely repayments, can increase your chances of approval for a home loan. On the other hand, a poor credit history or a history of defaults and bankruptcies may make it harder to secure a loan or result in higher interest rates.
Government Policies and Home Loan Interest Rates
Government policies play a significant role in influencing home loan interest rates. Changes in regulations, tax incentives, and other governmental actions can directly impact the cost of borrowing for individuals seeking a home loan.
Impact of Government Regulations
Government regulations can affect home loan interest rates by imposing restrictions on lending practices, setting guidelines for financial institutions, and influencing the overall economic environment. For example, changes in monetary policy by the central bank can lead to fluctuations in interest rates, thereby affecting the rates offered on home loans.
Recent Changes in Government Regulations
In recent years, there have been various changes in government regulations that have impacted home loan interest rates. For instance, the implementation of stricter lending standards following the financial crisis led to higher interest rates for riskier borrowers. Additionally, initiatives to promote affordable housing may have resulted in lower interest rates for certain qualifying borrowers.
Impact of Tax Incentives
Tax incentives provided by the government can also influence home loan interest rates. For example, tax deductions on mortgage interest payments incentivize homeownership and can lead to lower effective interest rates for borrowers. These incentives can make borrowing for a home more affordable and attractive for potential buyers.
Strategies for Managing Home Loan Interest Rates
When it comes to managing home loan interest rates, there are several strategies that borrowers can consider to secure better rates and save on interest payments. Refinancing home loans, understanding interest rate lock-ins, and knowing when to switch lenders are key strategies that can help borrowers effectively manage their home loan interest rates.
Refinancing Home Loans
Refinancing a home loan involves replacing an existing loan with a new one, typically with more favorable terms such as lower interest rates. This strategy can help borrowers reduce their monthly payments, save on interest costs over the life of the loan, or even shorten the loan term. However, it’s important to carefully consider the associated costs and benefits of refinancing before making a decision.
Interest Rate Lock-Ins
An interest rate lock-in is an agreement between a borrower and a lender to secure a specific interest rate for a specified period, typically until the loan closes. This can protect borrowers from potential interest rate increases during the loan approval process, providing them with peace of mind and financial security. It’s essential for borrowers to understand the terms and conditions of the lock-in agreement to make informed decisions.
Switching Lenders for Better Rates
There may be instances when it becomes advantageous for borrowers to consider switching lenders to secure better interest rates. Factors such as changes in the market conditions, improved credit score, or the availability of more competitive loan products can influence this decision. By comparing offers from different lenders and negotiating terms effectively, borrowers can potentially save money on interest payments and overall loan costs.
Understanding Home Loan Interest Rate Jargon
When dealing with home loan interest rates, it’s essential to understand the various terms associated with them. Common terms like APR, points, and margin play a crucial role in determining the overall cost of a home loan and can significantly impact monthly mortgage payments.
APR (Annual Percentage Rate)
The APR represents the total cost of borrowing, including the interest rate and additional fees. It provides a more accurate picture of the loan’s true cost compared to just the interest rate.
Points
Points are upfront fees paid to the lender to reduce the interest rate on the loan. One point is equal to 1% of the loan amount, and paying points can lower monthly payments over the life of the loan.
Margin
The margin is a fixed percentage added to the index rate to determine the interest rate on an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM). It remains constant throughout the life of the loan and influences how much the rate can fluctuate with changes in the index.
Final Summary
Navigating the landscape of home loan interest rates can seem daunting, but armed with the right knowledge, you can make confident and informed decisions that align with your financial goals. Whether you’re a first-time homebuyer or a seasoned homeowner looking to refinance, staying informed about these rates is key to a successful financial future.